Nearly a million evacuated as Philippines braces for ‘super typhoon’
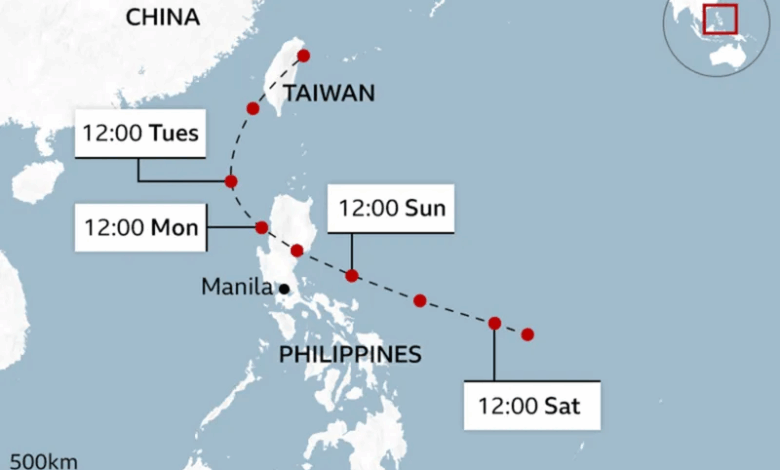
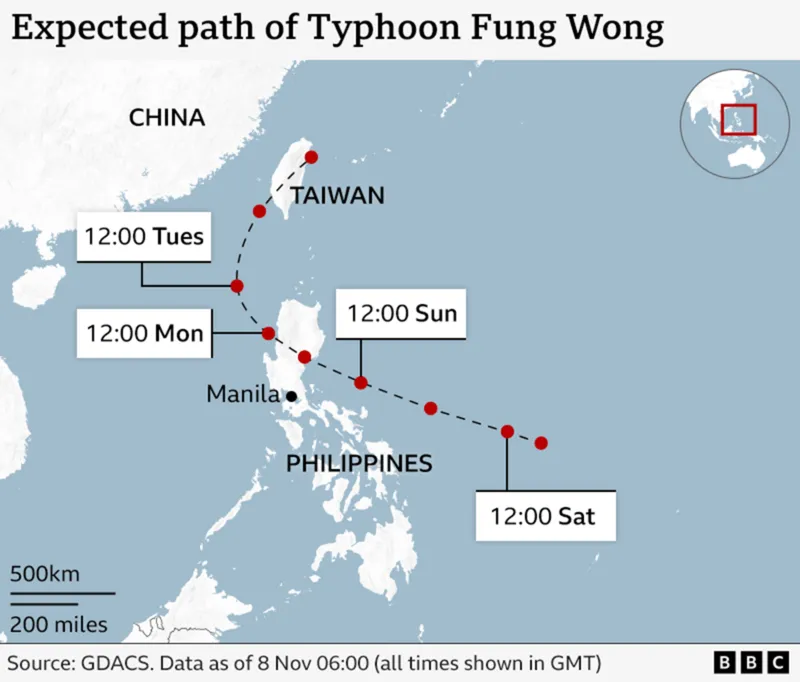
More than 900,000 people have been evacuated in the Philippines ahead of Typhoon Fung-wong, which is expected to make landfall on Sunday evening.
The storm was upgraded to super typhoon with sustained winds of around 185 km/h (115mph) and gusts of 230km/h (143mph), according to the country’s meteorological service.
The eastern Bicol region was the first part of the Philippines to be directly hit by the storm on Sunday morning, with Luzon – the country’s main population centre – expected to be hit by Sunday night.
Fung-wong – known locally as Uwan – comes days after an earlier storm, Kalmaegi, left a trail of destruction and nearly 200 people dead.
Several schools have either cancelled classes on Monday or moved them online, while nearly 300 flights have been cancelled.
Fung-wong is expected to weaken after making landfall somewhere between the districts of Baler and Casiguran, but it is likely to remain a typhoon as it travels over Luzon.
Over 200mm of rain is forecast for parts of Luzon, with even 100-200mm in the Metro Manila area. This is expected to cause severe flooding and landslides.
Eastern parts of the Philippines have already begun experiencing heavy rains and winds, a weather official said on Saturday evening.
While much of the country is expected to be affected, there are particular concerns about those areas that could take a direct hit, including Catanduanes, an island in the east of the Bicol region, where extreme conditions were reported on Sunday morning.
Residents there, as well as in other low-lying and coastal areas, had been urged to move to higher ground by Sunday morning.
In the Aurora region, in eastern Luzon, BBC News spoke to Hagunoy, 21, who works at one of the dozen hotels which line the coast in Sabang.
He said police had repeatedly visited in recent days to ensure all guests were evacuated ahead of the storm. The hotels were all deserted on Sunday morning.
While the tide had risen sharply, Hagunoy said he would stay as long as he could to guard the property, before riding his motorbike home to safety.
Staff had secured the gates and tied windows shut with rope to try to stop the glass from shattering in the wind.
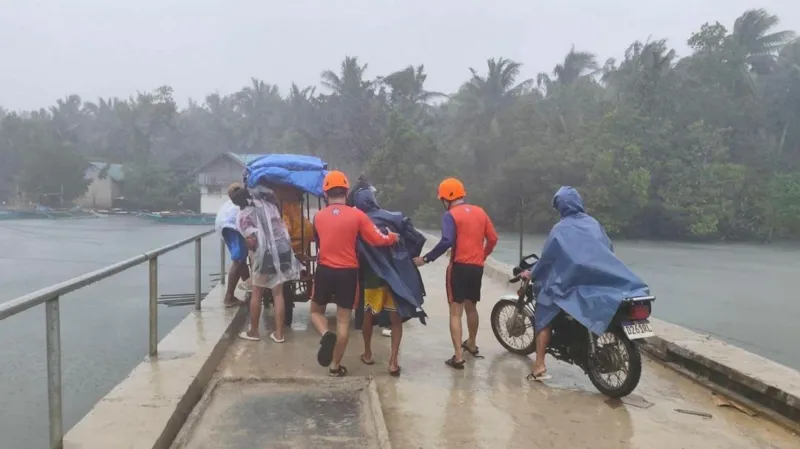

In central Aurora more than 200 people arrived at a shelter in a sports centre. Many parents have brought young children, too young to remember Typhoon Haiyan, which killed more than 6,000 people when it struck the Philippines in 2013.
Fung-wong has also forced the suspension of rescue operations following the passage of Kalmaegi, one of the strongest typhoons this year.
Heavy rainfall sent torrents of mud down hillsides and into residential areas. Some poorer neighbourhoods were obliterated by the fast-moving flash floods.
At least 204 people are now known to have died in the Philippines as a result of the earlier storm, while more than 100 are still missing.
Five people also died in Vietnam, where strong winds uprooted trees, tore off roofs, and smashed large windows.
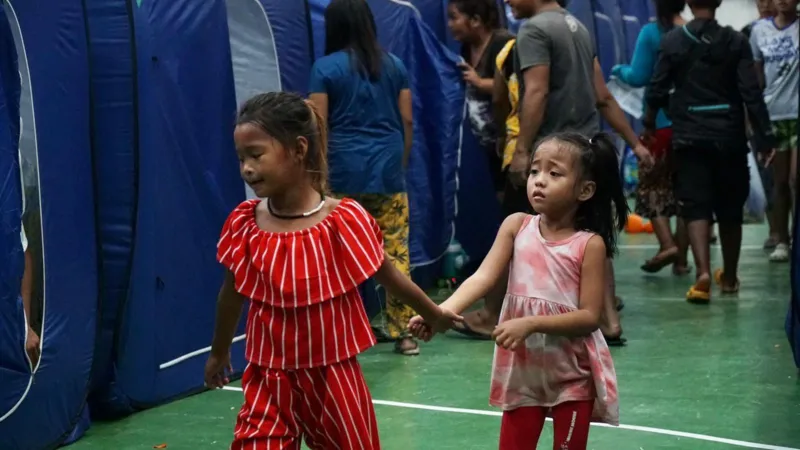

The Filipino government declared a state of calamity across the country after Typhoon Kalmaegi and in preparation for the coming storm.
It has given government agencies more power to access emergency funds and fast-track deliveries of essential goods and services.
For some Filipinos, the devastation wrought by Kalmaegi has left them even more anxious about the storm to come.
“We decided to evacuate because the recent typhoon brought floods in our area, and now I just want to keep my family safe,” Norlito Dugan told the AFP news agency.
He is among those who have taken shelter in a church in the city of Sorsogon in Luzon.
Another resident, Maxine Dugan, said: “I’m here because the waves near my house are now huge.”
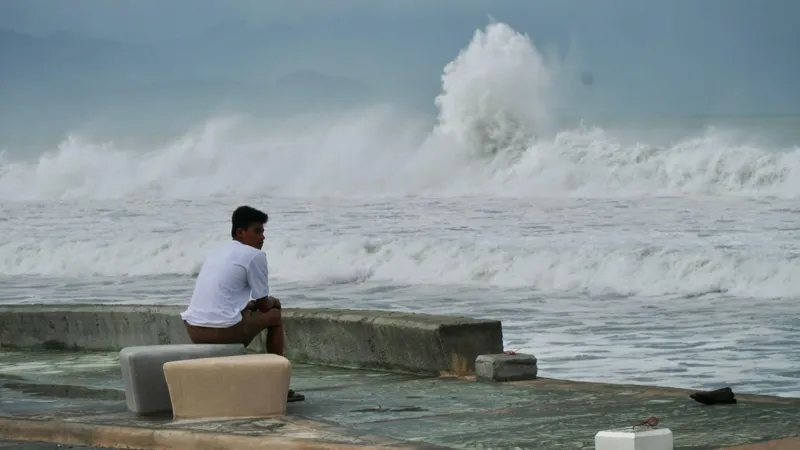

The Philippines – located near the area where Pacific Ocean tropical weather systems form – is one of the most vulnerable countries in the world to cyclones.
About 20 tropical cyclones form in that region every year, half of which affect the country directly.
Climate change is not thought to increase the number of hurricanes, typhoons and cyclones worldwide.
However, warmer oceans coupled with a warmer atmosphere – fuelled by climate change – have the potential to make those that do form even more intense. That can potentially lead to higher wind speeds, heavier rainfall, and a greater risk of coastal flooding.
DISCLAIMER: The Views, Comments, Opinions, Contributions and Statements made by Readers and Contributors on this platform do not necessarily represent the views or policy of Multimedia Group Limited.
DISCLAIMER: The Views, Comments, Opinions, Contributions and Statements made by Readers and Contributors on this platform do not necessarily represent the views or policy of Multimedia Group Limited.
Source link





